France has built a global reputation not only for academic excellence, but also for making high-quality higher education financially accessible. Unlike many popular study destinations, France combines world-class institutions, state-regulated tuition fees, and a wide ecosystem of scholarships and financial aid.
For international students, however, understanding the real cost of studying in France goes beyond tuition alone. It requires clarity on fees, living costs, scholarships, and funding strategies.
Tuition Fees in France: What International Students Pay
Public vs Private Institutions
France’s higher education system is divided between public institutions, funded by the state, and private institutions, which set their own fees.
Tuition Fees at Public Institutions
Public universities and many Grandes Écoles charge nationally regulated tuition fees, which remain low by global standards. Public universities and state-run institutions under the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research apply different tuition rates depending on a student’s nationality and enrolment status.
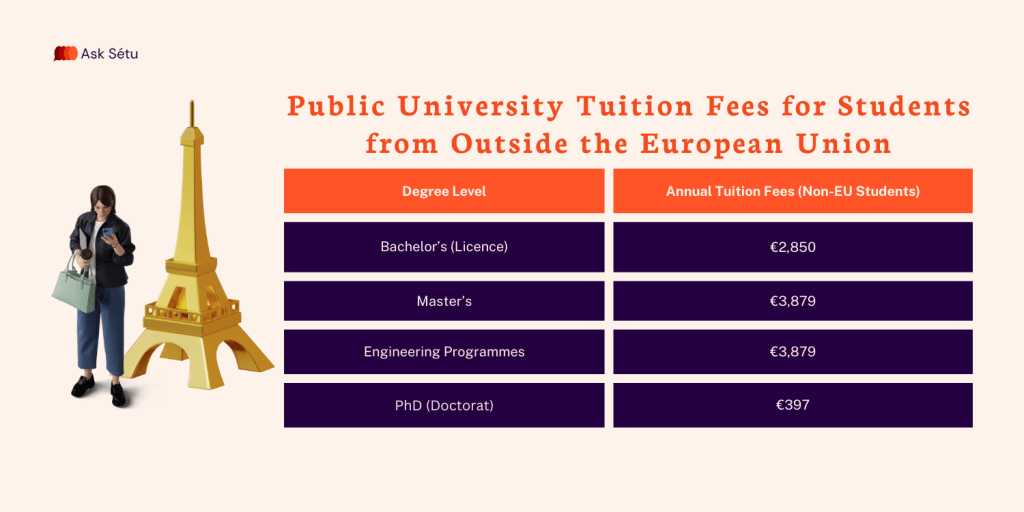
The French government covers a large share of the real cost of education, which exceeds €10,000 per student per year. The French state subsidises over 70% of the true cost of higher education per student. While non-EU tuition fees are higher than before, a wide range of exemptions and scholarships significantly reduces—or even eliminates—this cost for many students.
Tuition Exemptions
Non-EU students may qualify for partial or full tuition exemptions if they:
- Are awarded government or institutional scholarships
- Enrol in institutions that voluntarily apply fee waivers
- Are selected for strategic international partnerships
- Meet specific academic excellence or equity criteria
Tuition Fees at Private Institutions
Private institutions, particularly business schools, engineering schools, and specialised programs, set their own fees.
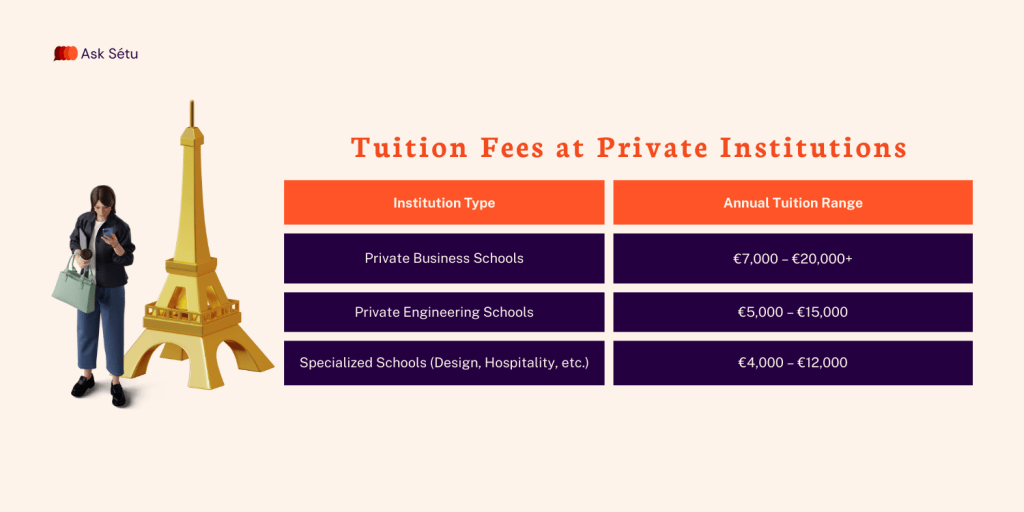
While more expensive, these institutions often offer:
- Strong industry connections
- English-taught programs
- Integrated internships and career placement
Cost of Living in France: A Realistic Budget
Tuition is only one part of the equation. Students must also budget for living expenses, which vary by city.
Average Monthly Living Costs
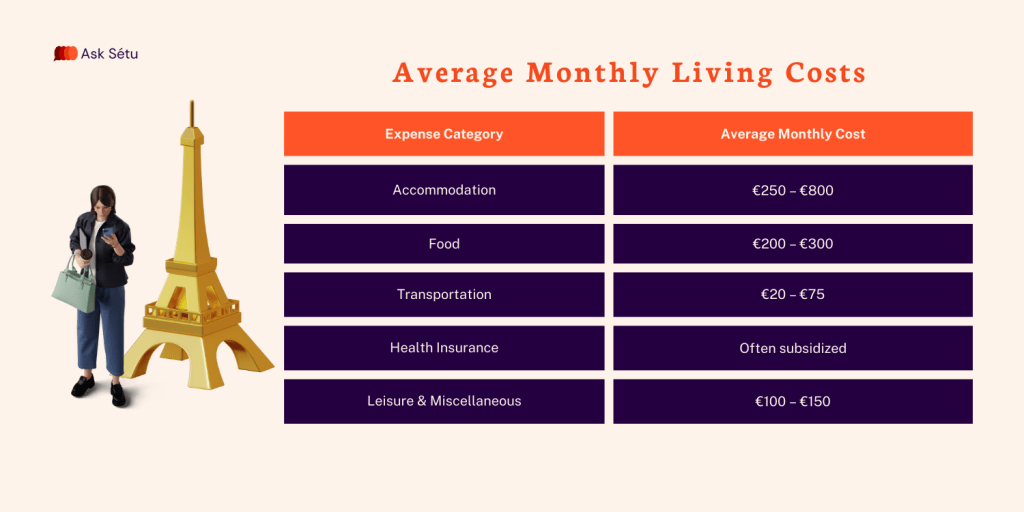
Estimated average: €700–€1,000 per month. Paris sits at the higher end; regional cities are more affordable. Studying outside Paris can reduce living costs by up to 40% without compromising academic quality.
Scholarships in France: Funding Your Studies
France offers one of Europe’s most structured and transparent scholarship ecosystems, coordinated in large part by Campus France.
Major National Scholarship Programs
1. Eiffel Excellence Scholarship
- Targeted at Master’s and PhD students
- Covers monthly allowance, travel, health insurance
- Highly competitive
“The Eiffel Scholarship aims to attract top international students to French degree programs.” — French Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs
2. Charpak Scholarship
- Designed for students from select countries, like India
- Supports tuition, living expenses, and mobility
3. Campus France Excellence Scholarships
- Country-specific and institution-specific awards
- Often co-funded with universities or regions
Institutional & Regional Scholarships
Many French institutions and local governments offer:
- Merit-based scholarships
- Need-based grants
- Tuition waivers
- Housing subsidies
Over 40% of international students in France receive some form of financial support.
Can International Students Work While Studying?
Yes. International students are allowed to work up to 964 hours per year (approximately 20 hours per week).
Typical student wages are in the range of €9 to €11 per hour (minimum wage indexed), but more skilled jobs can go up to €20 per hour. Baby-sitting and pet-sitting is a popular gig among students, and they can earn anything from €6 to €40 for the sitting, based on the duration and complexity of the sitting.
While not a primary funding source, part-time work can meaningfully offset daily expenses.
Smart Funding Strategies for Studying in France
To maximize affordability:
- Apply early for scholarships
- Target public institutions where possible
- Choose cities with lower living costs
- Combine scholarships + part-time work + other financial aid available to international students
The Bigger Picture: France’s Value Proposition
Even at the updated non-EU tuition levels, a Master’s degree in France (€3,879/year) remains far below UK (£10,000–£25,000/year) and US ($20,000–$50,000/year). PhD tuition is among the lowest in Europe. Living costs are mitigated by student healthcare systems, subsidised public transport, and other financial aid.
Studying in France continues to be a high-return educational investment – academically, professionally, and financially.
Planning to study in France?
Ask Sétu is here to guide you through admissions, scholarships, and life in France. Explore your options with AI-powered tools, expert tips, and real student stories…so you can focus on building your future.


Leave a comment